Agenda:
What is Agile:
Scrum:
History of Scrum:
Characteristics:
How Scrum works:
Waterfall Vs. Scrum:
Scrum Framework:
Product Owner:
Scrum Master:
Picking Scrum Master:
Ceremonies:
Sprint planning meeting:
Parts of Sprint planning Meeting:
Product Backlog:
Product Backlog Estimation with Planning Poker:
Sprint Backlog:
Sprints:
No Changes during the Sprint:
Daily Scrum:
Sprint Burndown Chart:
Sprint Dashboard:
Sprint Burndown Chart:
Sprint Review Meeting:
Sprint Retrospective Meeting:
- Introduction
- What is Agile methogology
- What is Scrum?
- Histroy of Scrum
- Functionality of Scrum
- Components of Scrum
- Scrum Roles
- The Process
- Scrum Artifacts
- Scaling Scrums
- Classical methods of software development have many disadvantages
- huge effort during the planning phase
- poor requirements conversion in a rapid changing environment
What is Agile:
- Agile methods are considered
- Lightweight
- people based rather than plan-based
- Agile methods
- Scrum
- Extreme Programming
- Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
- Dynamic System Development Method(DSDM)
- Agile Alliance(http://www.agilealliance.org/)
- A non-profit organization promotes agile development
Scrum:
- Scrum is an agile process that allows us to focus on delivering the highest business value in the shortest time
- It allows us to rapidly and repeatedly inspect actual working software (every two weeks to one month)
- The business sets the priorities. Our teams self-manage to determine the best way to deliver the highest priority features
- Every two weeks to a month any one can see real working software and decide to release it as is or continue to enhance for another iteration
History of Scrum:
- 1995
- Analysis of common software development processes
- Not suitable for unpredictable and non-repeatable processes
- Design of new method: Scrum by Jeff Sutherland & Ken Schwaber
- Enhancement of Scrum by Mike Beedle & combination of Scrum with Extreme Programming
- 1996
- Introduction of Scrum at OOPSLA conference
- 2001
- Publication "Agile Software Development with Scrum" by Ken Schwaber & Mike Beedle
- Successful application of Scrum in over 50 companies
- Founders are members in the Agile Appliance
Characteristics:
- Self-organizing teams
- product progresses in a series of month-long "sprints"
- Requirements are captured as list of items in the list of "product backlog"
- No specific engineering practices prescribed
- Uses generative rules to create an agile environment for delivering projects
- One of the "agile processes"
How Scrum works:
Waterfall Vs. Scrum:
Scrum Framework:
- Roles
- Product Owner
- Scrum Master
- Cross functional Team
- Ceremonies
- Sprint planning
- Daily Scrum meeting
- Scrum-of-Scrums
- Sprint Review
- Sprint Retrospection
- Artifacts
- Product Backlog
- Sprint Backlog
- Sprint Burndown chart
Product Owner:
- Defines the features of the product
- Decide on release date and content
- Be responsible for the profitability of the product (ROI)
- Prioritize features according to market value
- Adjust features and priority every iteration, as needed
- Accept or reject work results
Scrum Master:
- Represents management to the project
- Responsible for enacting Scrum values and practices
- Removes impediments
- Ensure that the team is fully functional and productive
- Enable close co-operation across roles and functions
- Shield the team from external interferences
Picking Scrum Master:
- Traits of an effective Scrum Master
- Highly committed to the success of the team
- Good people skills
- Good communication skills
- Observant, Good listener
- Courageous mindset
- Proactive, helpful personality
- Technical expertise helpful but not mandatory
- Best results will come from a full-time Scrum Master
- If dedicated person is not available, a team-member will have to play the role, and take a much lighter load of tasks
- Avoid having the team's manager be Scrum Master
- Typically 5-10 people
- Cross-functional
- QA, Programmers, UI Designers etc.,
- Members should be full-time
- May be expectations (e.g., System Admin etc.,)
- Teams are self-organizing
- Membership can change only between sprints
Ceremonies:
- Sprint planning meeting
- Sprint
- Daily Scrum
- Sprint Review meeting
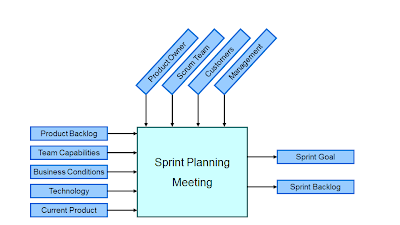
Sprint planning meeting:

Parts of Sprint planning Meeting:
- 1st Part: (Grooming)
- Creating Product Backlog
- Determine the Sprint Goal
- Participants : Product Owner, Scrum Master, Scrum Team
- 2nd Part:
- Participants : Product Owner, Scrum Master, Scrum Team
- Creating Sprint Backlog
Product Backlog:
- A list of desired work on the project
- List is prioritized by Product Owner
- Typically a Product Manager, Marketing Internal Customer, etc.,
- Requirements for a system, expressed as a prioritized list of Backlog items
- Is managed and owned by Product Owner
- Usually created during the Sprint Planning Meeting
- Can be changed and re-prioritized
Product Backlog Estimation with Planning Poker:
- Estimation of each user story in product catalog can be done as
- size = Effort x Complexity x Uncertainty
- Team make use of poker cards to estimate the user story
- Poker cards can have a
- Fibonacci order (0,1/2,1,2,3,5,8,13,20,40,80,100,∞,?)
Sprint Backlog:
- A subset of Product Backlog items, which defines the work for a Sprint
- Is created by Team members
- Each team has it's own status
- Should be updated everyday
- No more than 300 tasks in the list
- If a task requires more than 16 hours, it should be broken down
- Team can add or subtract items from the list
Sprints:
- Scrum projects make progress in a series of "Sprints"
- Target duration in one month
- +/- a week or two
- But, a constant duration leads to a better rhythm
- Each Sprint begins with the Daily Scrum Meeting
- Product is designed, coded, and tested during the sprint
- NO outside influence can interfere with the Scrum team during Sprint
No Changes during the Sprint:
- Plan sprint durations around how long you can commit to keeping change out of the Sprint
Daily Scrum:
- Parameters
- Daily
- 15 minutes
- Stand-up
- Not for problem solving
- Three questions
- What did you do yesterday
- What will you do today
- What obstacles are in your way?
- Chickens and Pigs are invited
- Help avoid other unnecessary meetings
- Only Pigs can talk
Sprint Burndown Chart:
- Depicts the total Sprint Backlog hours remaining per day
- Show the estimated amount of time to release
- Ideally should burndown to zero to the end of the Sprint
- Actually is not straight line
- Can bump up
Sprint Dashboard:
Sprint Burndown Chart:
Sprint Review Meeting:
- Team presents what is accomplished during the sprint
- Typically takes the form of a demo of new features or underlying architecture
- Participants
- Customers
- Management
- Product Owner
- Other engineers
Sprint Retrospective Meeting:
- Scrum Team only
- Feedback meeting
- Usually lasts 1-2 hours
- Make 4 lists
- what went well (During the sprint)
- What could have been better (During the sprint)
- Things to try (To do better in the next sprint)
- Issues to escalate (To Upper Management)
Scalability of Scrum:
- A typical Scrum team is 6-10 people
- Jeff Sutherland - up to over 800 people
- "Scrum of Scrums" or what called "Meta-Scrum"
- Frequency of meetings is based on the degree of coupling between packets








No comments:
Post a Comment